Biology 2018
Objective Questions
The scientist who introduced binomial nomenclature in the classification of organisms was
Correct Answer: A) Carolus Linnaeus.
Which of the following statements is true about arthropods?
Correct Answer: B) Prothorax bears only legs
What level of organization is Spirogyra?
Correct Answer: D) Cell
The streaming movement of cytoplasm within Paramecium is known as
Correct Answer: B) cyclosis.
Which of the following organelles is found only in plant cells?
Correct Answer: C) Plastids
Active transport differs from diffusion in that active transport
Correct Answer: C) allows the movement of substances against concentration gradient.
The diagrams below are illustrations of an experimental set-up to demonstrate a type of tropic response in plants. Study them and answer questions 7 to 8.
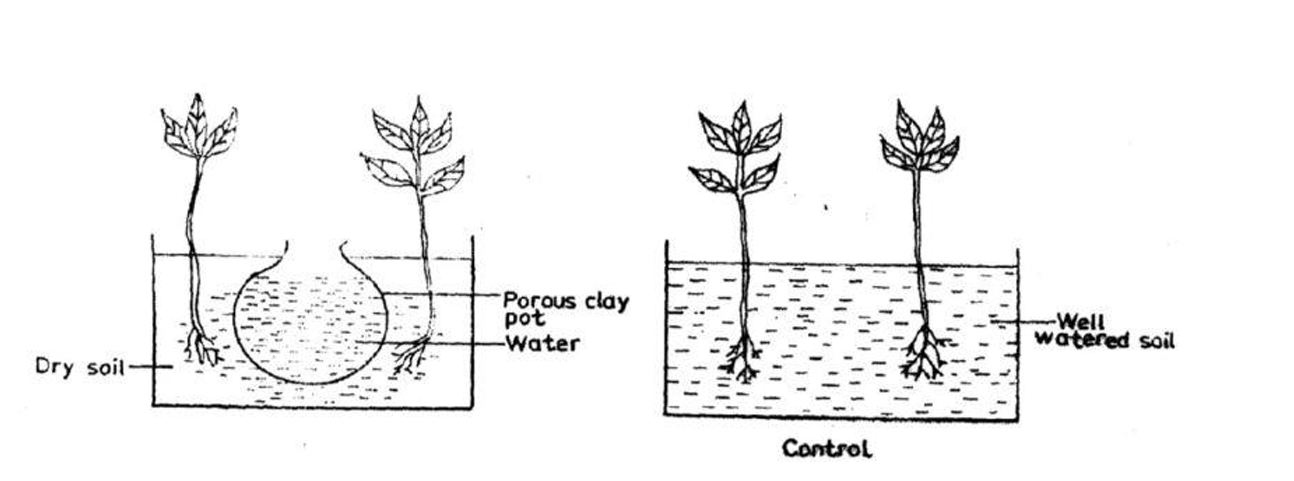
The type of response demonstrated is
Correct Answer: D) hydrotropism.
The conclusion drawn from the experiment is that
Correct Answer: C) roots of plants are positively hydrotropiC)
The odontoid process is found on the
Correct Answer: B) axis vertebrA)
A seedling was made to stand in a solution of red ink for three hours and a transverse section of the stem was examined under the microscope. The process being investigated was
Correct Answer: B) diffusion of coloured substances.
Which of the following structures would carry out respiration?
Correct Answer: B) germinating cowpea
Which of the following substances is not an excretory product of animals?
Correct Answer: C) Oxygen
An example of homeostasis in living organisms is
Correct Answer: B) the release of phosphorous into the phloem of a plant growing in a phosphorus-deficient soil.
Ultrafiltration in the kidney takes place in the
Correct Answer: C) Bowman's capsule.
The thyroid gland is located at the base of the
Correct Answer: A) neck.
Which of the following statements about the response of neurones to stimulus is correct? The
Correct Answer: A) intensity of stimulus must reach a threshold value before the neurone can be exciteD)
Which of the following practices may lead to infection of the eye? Use of
Correct Answer: B) contact lenses
The structures for gaseous exchange in breathing roots are
Correct Answer: A) lenticels.
The diagram below is an illustration of the life cycle of an insect. Study it and answer questions 19 and 20.
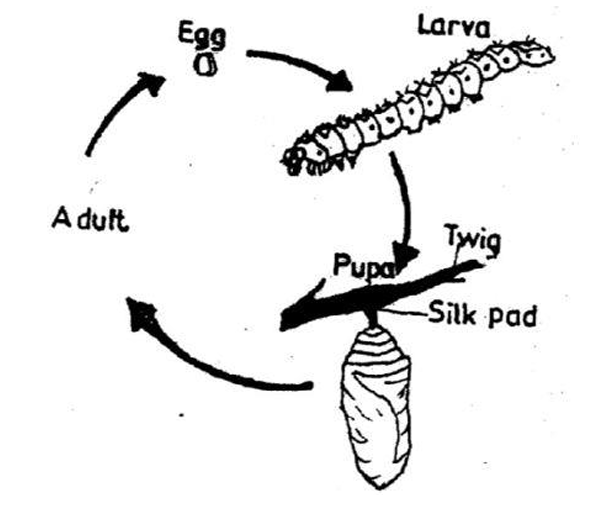
The adult insect in this life cycle is
Correct Answer: C) butterfly.
The larva is also known as
Correct Answer: B) caterpillar.
The source of energy required by plants during food production is
Correct Answer: B) sunlight.
One major difference between plant and animal nutrition is the ability of plants to synthesize
Correct Answer: D) food for plants and animals.
By what process is starch converted into maltose?
Correct Answer: C) Hydrolysis
The ascent of water in tall trees is mainly due to
Correct Answer: C) transpiration pull.
The duodenum of a person was surgically removeD) Which of the following food substances would have their digestion affected?
Correct Answer: A) Starch, protein and lipids
Which of the following dental formulae represents the dentition in rabbits?
Correct Answer: A) I2/1 C0/0 P3/2 M3/3
The diagram below is an illustration of an experimental set-up to demonstrate a property of soil. Study it and answer questions 27 and 28.
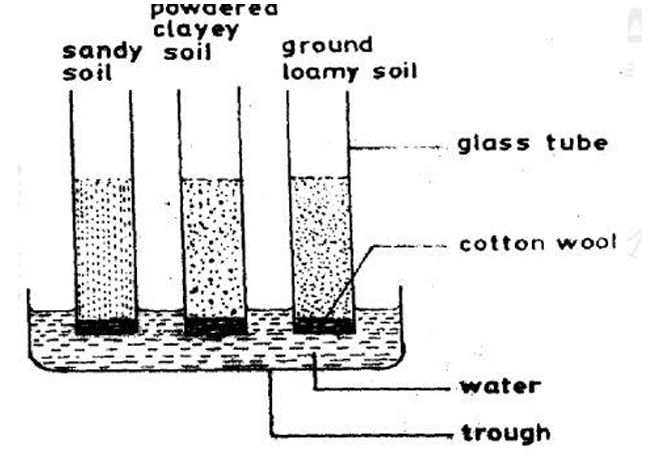
The property of soil demonstrated is
Correct Answer: C) capillarity.
Which of the following statements would be a correct observation at the end of the experiment? Water moves
Correct Answer: A) highest in clayey soil.
The most important factor(s) that influence(s) the ecological niche of an organism is/are the
Correct Answer: C) competition for food and space.
The diagram below is an illustration of organisms in an air-tight aquarium. The most important factor needed by the organisms is
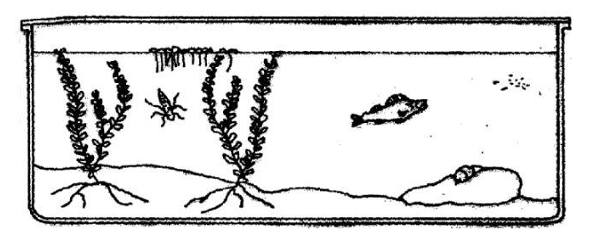
Correct Answer: B) light energy.
Which of the following instruments is used to determine the turbidity of water?
Correct Answer: A) Secchi disc
In an ecosystem, the least efficient energy transfer link is from the
Correct Answer: B) secondary consumers to decomposers.
Xerophytes have the following characteristics aimed at conserving water except
Correct Answer: B) broad leaf surfaces.
An association between living organisms in which one lives on and feeds at the expense of the other is known as
Correct Answer: A) parasitism.
When large numbers of organisms share limited space and resources: the immediate result is
Correct Answer: D) competition.
Which of the following diseases is caused by a bacterium?
Correct Answer: B) Syphilis
Conservation of wildlife is necessary mainly because
Correct Answer: D) it prevents the extinction of species.
Two unconscious patients X and Y whose blood genotypes are AO
and AB respectively were
transfused with blood from the same donor. Patient X
immediately showed signs of difficulty in
breathing while patient Y showed no negative reaction.
Use the information above to answer questions 38 and 39
Patients X and V were likely transfused with blood of genotype
Correct Answer: A) BO.
What should the hospital have done to prevent patient X from showing the symptom described above? Patient X should have
Correct Answer: C) undergone an agglutination test.
The greatest contribution to genetic studies was made by
Correct Answer: D) Gregor Mendel.
The exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes is called
Correct Answer: D) crossing over.
The diagrams below are illustrations of the inheritance of
coat colour in mice. J, K, L, M and N are
parents. The
cross between two parent mice gave rise to offspring P, Q, R
and S.
Study the diagrams and answer questions 42 and 43.
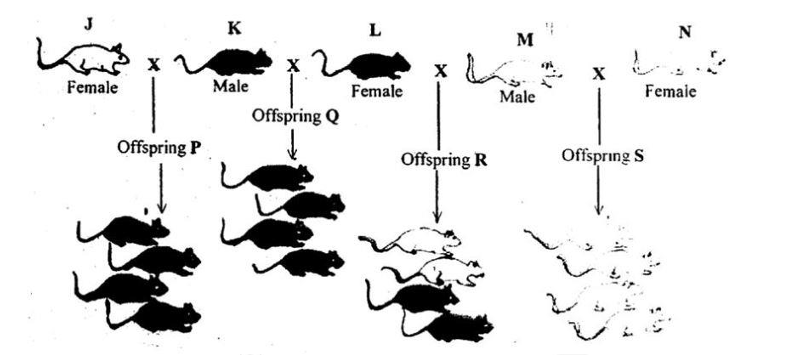
Which parent mouse is heterozygous for coat colour?
Correct Answer: D) J
Which of the offspring are all homozygous?
Correct Answer: A) S
Genes that remain linked are those
Correct Answer: A) close to each other on the chromosomes.
A plant cell has 14 chromosomes prior to mitosis. What is the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells?
Correct Answer: C) 14
The chemical bond that holds the bases of the two strands of DNA together is
Correct Answer: C) hydrogen bonD)
The diagram below is an illustration of one the theories of evolution. Study it and answer questions 47 and 48.
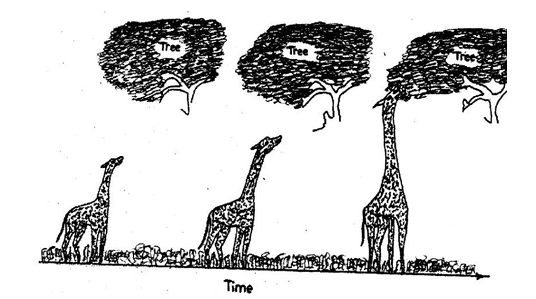
The diagram below is an illustration of one the theories of evolution. Who proposed the theory in the illustration?
Correct Answer: C) Jean Lamarck
The theory supports
Correct Answer: B) the use and disuse of body parts.
In evolution, fossils are naturally preserved in
Correct Answer: B) rocks.
Which of the following insects is not a social insect?
Correct Answer: D) Housefly
Theory Questions
(a)Explain briefly how the structure of
each of the following cells relate to their
functions:
(i)sperm cell; [4 marks]
(ii) palisade cell. [4 marks]
(b)Make a drawing, 8 cm – 10 cm long of the front view of
the female reproductive system in humans and label fully. [8
marks]
(c)State two differences between
reproduction in mammals and in amphibians. [2 marks]
a) Name the gases involved in the photosynthesis of a
plant [2 marks]
(b)State one role each
of the gases named in 2(a) [2
marks]
(c)
(i)What is a variegated leaf? [1 mark]
(ii) Which part of the variegated leaf would test
positive when treated with iodine solution? [1 mark]
(iii)State two reasons for the answer
in 2(c)(ii). [2 marks]
(iv)Name one mineral element required
by plants for the formation of the part that would test
positive in 2(c)(ii). [2 marks]
(d)The table below indicates different methods by which
organisms obtain food. Place the following organisms
under the headings in the table below:
Human, Mushroom, Venus flytrap, Waterleaf plant, Tapeworm, Elephant grass, Housefly, Lichen, Spirogyra, Rhizopus.
Mode of Nutrition |
||||
Holozoic |
Parasitic |
Symbiotic |
Saprophytic |
Autotrophic |
[10 marks]
(a) Explain briefly the following terms:
(i)renewable natural resources;
(ii)non-renewable natural resources. [4 marks]
(b)Give two examples each
of:
(i)renewable natural resources;
(ii)non-renewable natural resources [4 marks]
(c) State five ways of conserving forests.
[5 marks]
(d) State four effects of adding animal
manure to garden soil. [4 marks]
(e) Give the possible genotypes in humans.[3 marks]
(a)Explain briefly the following terms:
(i)gene;
(ii) hybrid;
(iii) trait.[6 marks]
(b) Two heterozygous yellow flowers are crossed. Using a
genetic diagram, state the phenotypic and genotypic ratios
of the first filial generation. [10 marks]
(c) State four transmittable characters in
plants. [4 marks]
(a)
(i)Explain briefly chemosynthesis as
a mode of nutrition [3 marks]
(ii) Give two examples of organisms that
carry out chemosynthesis [2 marks]
(b)List three gases in the atmosphere with
their percentage composition.
Gases in the atmosphere |
Percentage composition |
[6 marks]
(c)
(i)State four characteristics of a
salt marsh habitat. [4 marks]
(ii)Explain briefly how plants are modified
for anchorage in a salt marsh habitat. [2 marks]
(d)
(i)List four bacterial diseases
associated with poor food hygiene. [4 marks]
(ii)State three effects of poor food
hygiene. [3 marks]
(e)A person was involved in a car accident and became
unconscious due to excessive blood loss. Explain
briefly how the blood lost could be
restored. [3 marks]
(f) State three differences between tillage and bush burning as farming practices.
Tillage |
Bush burning |
[3 marks]
Practical Questions
List of Specimen
Specimen A - Fresh/wet preserved mosquito larva in a Petri dish containing water.
Specimen B - Fresh/wet preserved maggot in a Petri dish containing water.
Specimen C - Gill of fish (freshly procured) in a Petri dish containing water.
Specimen D - Lung of a small mammal (freshly preserved).
Specimen E - Dicotyledonous leaf (freshly plucked).
Specimen F - Membranous wing of a Cockroach.
Specimen K - Flower of Pride f Barbados or Caesalpinia.
Specimen L - Mature Elephant grass or Guinea grass.
Specimen M - Flower of Hibiscus plant.
Study specimens A and B and answer questions 1(a) to 1 (c)
(a)
(i)Name the habitat of each of
specimens A and B. [2
marks]
(ii)Name the adult stage into which
each of specimens A
and B would develop. [2 marks]
(iii)Name the phylum and class common
to the adult stages of specimens A and
B. [2 marks]
(b) State three observable features of
biological significance in:
(i) Specimen A; [6 marks]
(ii)Specimen B.[6 marks]
(c)(i)State four observable structural
differences between specimens A and
B. [4 marks]
(ii) State three observable
similarities between specimens A and
B.[3 marks]
Study specimens C, D and E and answer questions 2(a) to 2(c).
(a)
(i)Name the organism from which
each of specimens C,
D and E are obtained.
[3 marks]
(ii)State the function common to
specimens C, D and E.
[1 mark]
(iii)State three observable features
which adapt specimen C to its
function.[6 marks]
(b)
(i) State two observable
structural similarities in specimens C
and D.[3 marks]
(ii)State three observable structural
differences between specimens C and[3
marks]
(c)Make a drawing, 6 cm to 8 cm long of specimen
C and label fully. [9 marks]
Study specimens K and L and answer questions 4(a) to 4(f).
(a)
(i) Name the floral parts of specimen
K. [4 marks]
(ii)Indicate the number of floral parts in
each whorl of specimen
K.[4 marks]
(b)
(i) Name the sex of specimen K. [1
mark]
(ii)Give one reason for the answer in
4(b)(i) [1 mark]
(c)
(i)What is the symmetry of specimen
K? [1 mark]
(ii)Give one reason for the answer in
4(c)(i) [1 mark]
(d) Name one pollinating agent of
each of specimens K and
L. [2 marks]
(e) State four observable differences
between specimens K and L
[4 marks]
(f)Make a drawing 8 cm – 10 cm long of the
longitudinal section of specimen
K and label fully.[12 marks]